How To Calculate Total Variable Costs: Examples And Formulas
So, if the company produces more or less, the cost will increase or decrease proportionally. A clear example of a variable cost in a manufacturing context is the cost of raw materials used in the production process. As the level of output increases, the cost of raw materials also increases. Activity-based costing is a method of assigning costs to products or services based on the activities that go into producing them. This method is more accurate than traditional costing methods because it takes into account the different activities involved in producing a product or service.
Variable costs and fixed costs
These can include parts, cloth, and even food ingredients required to make your final product. A (relatively) painless rundown of the double-entry system of accounting, and why your business should probably switch to it immediately. Take your learning and productivity to the next level with our Premium Templates.

Would you prefer to work with a financial professional remotely or in-person?
This analysis calculates the contribution margin, which is the amount of revenue that is left over after deducting variable costs. By analyzing the contribution margin, businesses can identify which products or services are most profitable and make informed decisions about their product mix. Variable costs are expenses that change in proportion to the level of production or sales.
Great! The Financial Professional Will Get Back To You Soon.
Based in Atlanta, Georgia, William Adkins has been writing professionally since 2008. He writes about small business, finance and economics issues for publishers like Chron Small Business and Bizfluent.com. Adkins holds master’s degrees in history of business and labor and in sociology from Georgia State University. Apps like PayPal typically charge businesses per transaction so customers can check out purchases through the app.
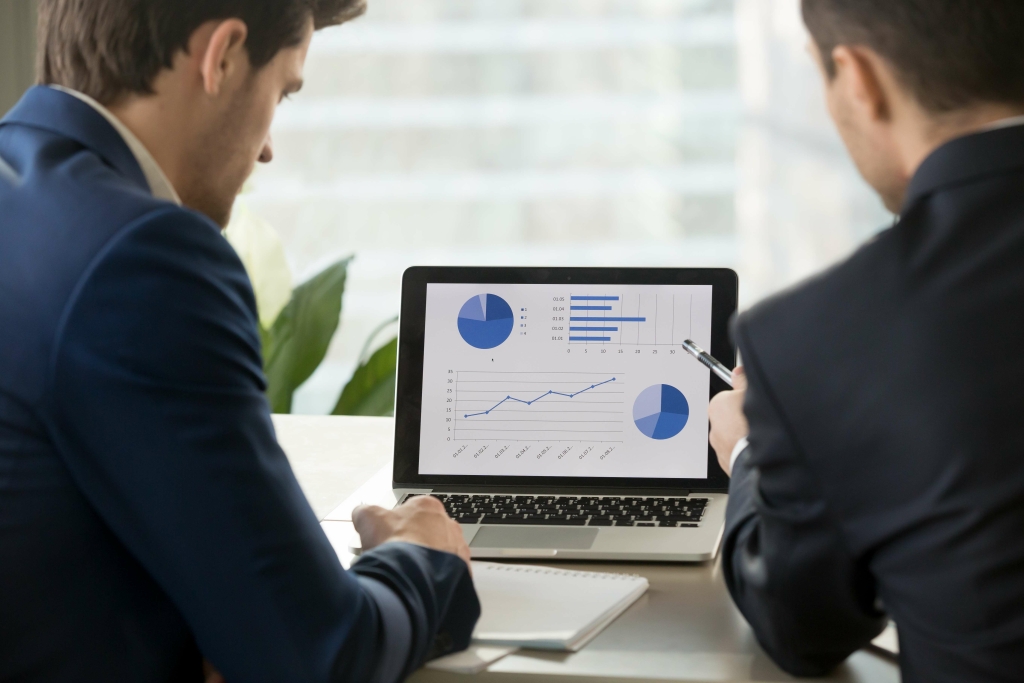
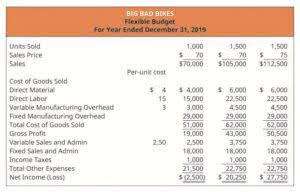
As production levels increase, more materials may be required, resulting in higher material costs. In conclusion, the total variable cost increases from $10k to $20k at a production level of 100 and 200 units, respectively. By multiplying the average variable cost by the quantity of units (or production), the total variable cost is $10k. To analyze the incremental change in the variable cost (and total cost) at various production levels, we’ll set up a table in Excel that ranges from 100 units to 200 units. In practice, cost structure analysis refers to the disaggregation of a specific company’s cost composition into fixed costs and variable costs.
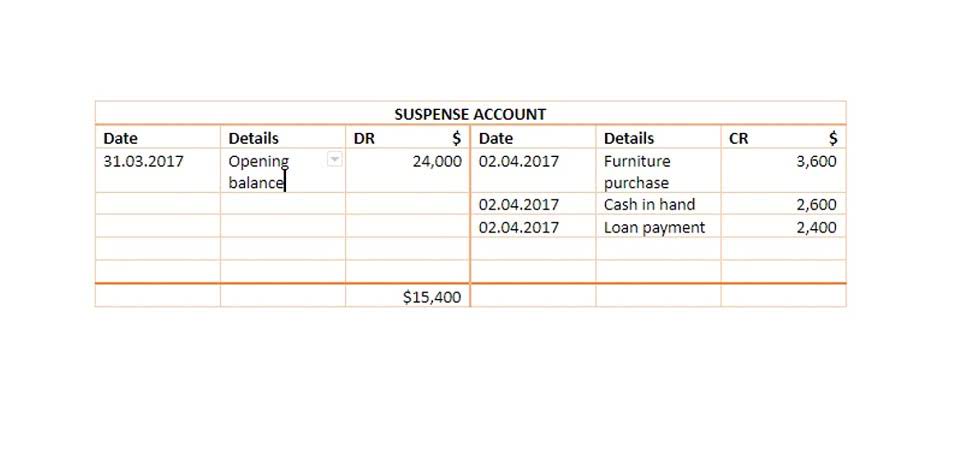
Average Variable Cost
Businesses live or die based on sales volume and how well they control costs. However, before you can effectively manage expenses and eliminate waste, you have to know what your business is spending and for what. Tracking variable costs is an essential part of this management function. Such costs comprise a major price per item formula part of overall operating expenses and help determine whether or not a product is profitable. As mentioned earlier, business costs consist of both fixed and variable costs depending on your work line, type of business, and industry. Variable expenses do not remain consistent if the output product changes.
- Sales commissions, for example, are also considered variable because the size of a commission is tied to the volume of products sold by an employee.
- These can include parts, cloth, and even food ingredients required to make your final product.
- Utilities are a variable cost because they usually increase and decrease alongside your production.
- Understanding the total variable costs and the fixed costs of your business is important for a variety of different reasons.
- It specifically measures the change in total cost when production output increases by one unit.
Direct materials refer to any materials that are used in the production of a unit that makes it into the product itself. For example, wood is a direct material for the chair company, since the final chair is made of it. Wood is considered a variable cost because the price of it can change over time.
- Although fixed costs can change over a period of time, the change will not be related to production, and as such, fixed costs are viewed as long-term costs.
- It can also be tricky for seasoned business professionals, so don’t get frustrated if it hasn’t clicked yet.
- An example of a variable cost per unit would be if a company makes chairs.
- Cutting costs by sourcing lower-quality raw materials can reduce variable costs in the short term but might harm the brand’s reputation and customer trust in the long run.
- Typically, variable costs are the first thing to get cut when companies want to increase profit margin.
- These are costs composed of a mixture of both fixed and variable components.
- As sales increase, more commissions may need to be paid out to employees or sales representatives.
- Calculating variable costs is an essential aspect of running a successful business.




